Learn how advanced engineering simulation tools can be used in product development to test, analyze and optimize designs even before manufacturing a single prototype.
In the recent past, engineers relied on a combination of manual calculations, physical prototyping, empirical testing, and theoretical analysis to develop new products. While these methods were effective, they were often time-consuming, resource-intensive, and limited in their ability to explore a wide range of design alternatives or complex simulations.
The introduction of virtual prototyping and simulation has significantly transformed the engineering landscape by providing engineers with powerful tools to simulate, analyze, and optimize designs with greater accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
At Outdesign Co, we leverage virtual prototyping to virtually simulate a new design before manufacturing prototypes which helps cut down the number of physical prototyping iterations, identify any design flaws early on and quickly visualize different product variations. All this leads to faster, more cost-effective and sustainable product development.
Some commonly used engineering analysis tools used for virtual prototyping in new product development process:-
1) Thermal Analysis
Thermal simulation tools allow engineers to analyze heat transfer, thermal behavior, and temperature distribution within components, systems, or devices. This type of simulation is crucial in various industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, energy, and manufacturing, where understanding and managing thermal effects are critical for product performance and reliability.
Thermal simulation helps identify potential thermal issues early in the design phase and aids in developing better, more optimized products.

Image: Thermal analysis of components on a circuit board.
2) Structural Analysis
Structural analysis has a wide range of applications in various industries, the more general use case involves analyzing strength of components under specific loads. Industry-specific use-cases include crash test simulations for automotive industry, part strength to weight optimizations and fatigue life analysis for aircraft, optimizing performance and vibration analysis of industrial machinery, simulating mechanisms, drop test simulations for consumer products and more.
Structural analysis is an indispensable tool for engineers to predict, assess, and optimize the behavior of structures, ensuring their safety, reliability, and performance across diverse industries.

Image: Drop test analysis to optimize the structure of an electronics enclosure.
3) Fluid Dynamics Analysis
Fluid dynamics analysis helps engineers with simulating and analyzing the behavior of fluids (liquids or gases) as they interact with solid structures or other fluids. It has various applications in optimizing aerodynamics for aircraft as well as automobiles, in the energy sector for designing wind turbine blades, simulating fluid flow in pipelines, in medical device design for modeling blood flow in arteries or airflow in the respiratory system, in electronics enclosures for thermal management, in plastic manufacturing to simulate mold flow and many more.

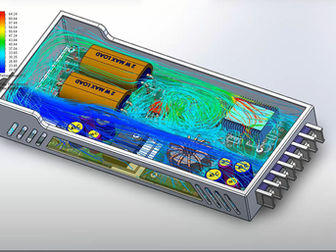
Image: CFD analysis to simulate airflow from fan and optimize cooling in an electronics enclosure.

Image: Mold flow - A specialized use case of fluid dynamics analysis used to optimize flow of molten plastic into a mold.
4) Electromagnetic Analysis
Electromagnetic analysis involves the simulation and evaluation of electromagnetic fields and their interactions with structures, devices, or materials. This analysis helps engineers understand, predict, and optimize electromagnetic behavior in various applications like designing PCBs (Printed Circuit boards), analyzing signal integrity, optimizing antenna design, studying electromagnetic wave propagation, analyzing wireless communication systems, evaluating the effects of electromagnetic fields in medical imaging devices like MRI machines or ensuring safety and compatibility of medical implants.

Image: Antenna design and simulation
5) Product visualization
3D product visualization serves as a powerful tool in every stage of product development, from ideation to marketing. It provides designers and stakeholders a visual representation of what the final product would look like and how it will function. Designers can quickly create multiple product variations digitally, showing the product in different colors, materials and finishes without having to create a physical prototype for each variation, thus speeding up the development process. High quality marketing assets like 3D renders and product animations can also be created faster and more cost-effectively than traditional photography.
Product visualization aids in decision-making, communication, and enhancing the overall product development lifecycle.

Image: 3D visualization of a consumer electronics product before prototyping.
To summarize, virtual prototyping offers multifaceted benefits in product development, significantly transforming the design process by providing a cost-effective, time-efficient platform to simulate, test, and refine product concepts.
It enables rapid iteration and validation of designs, expediting the identification and resolution of potential issues early in the development cycle. By eliminating the need for multiple physical prototypes, virtual prototyping drastically reduces associated costs and accelerates time-to-market, facilitating quicker design cycles and efficient decision-making.